In today’s digital-first business landscape, decisions can no longer rely on intuition or outdated processes. Organizations that consistently win—regardless of size—are those that transform raw data into clear, strategic action. Google Sheets has evolved into one of the most accessible and powerful platforms for doing exactly that.
This updated guide gives you a streamlined, modern, and SEO‑optimized walkthrough of how to use Google Sheets for data-driven decision making, advanced analysis, and clear reporting. You’ll also explore when specialized tools like Teamgate CRM provide deeper capabilities that spreadsheets alone cannot match.
Key Takeaways:
- Make Better Decisions with Data: Learn why moving beyond intuition leads to more predictable, profitable outcomes.
- Google Sheets as an Analytics Hub: Discover how to use Sheets for cleaning, analyzing, and visualizing complex datasets.
- Build a Solid Data Foundation: Import, structure, and validate data for accurate insights.
- Unlock Advanced Tools: Use QUERY, pivot tables, add-ons, and Apps Script to automate and scale your analysis.
- Create Insightful Dashboards: Design reports that influence stakeholders and communicate insights clearly.
- Explore Alternatives: Understand when tools like Teamgate CRM offer a more strategic analytics environment for sales teams.
Contents:
- Understanding Data-Driven Decision Making
- Introduction to Google Sheets as a Data Analysis Tool
- Setting Up Your Data Environment in Google Sheets
- Analyzing Data in Google Sheets
- Advanced Google Sheets Features for Data Analysis
- Crafting Insightful Reports and Dashboards
- Exploring Alternatives: Teamgate CRM’s Sales Insights and Analytics
- Conclusion
- FAQs: Google Sheets for Analytics
Understanding Data-Driven Decision Making
Data-driven decision making (DDDM) represents a transformative approach in the business world, moving away from intuition-based strategies to ones rooted in empirical evidence and analytics. This pivotal shift enables organizations to navigate the complexities of the modern market with precision and insight. Let’s delve deeper into the essence of DDDM, its differentiation from traditional decision-making processes, and the significant advantages it offers.
Traditional vs. Data-Driven Decision Making
Traditional Approach:
- Relies on experience, intuition, and subjective observation.
- Highly vulnerable to bias and inconsistent outcomes.
- Slow to adapt to evolving market conditions.
Data-Driven Approach:
-
- Uses real-time data and analytics to guide decisions.
- Enables objective evaluations of trends, performance, and opportunities.
- Supports strategic planning, forecasting, and more accurate risk management.
The Benefits of Data-Driven Decision Making
- Greater Market Agility: Respond to market changes quickly using live data.
- Improved Customer Experiences: Tailor offerings based on behavioral and demographic insights.
- Operational Efficiency: Identify bottlenecks and waste to optimize processes.
- Continuous Innovation: Use insights to spark new product ideas and uncover untapped markets.
By embracing data-driven decision making, organizations can transcend the limitations of traditional approaches, leveraging data to unlock unparalleled opportunities for efficiency, growth, and innovation. This strategic pivot is not just about adopting new tools and technologies but about fostering a culture that values data as a fundamental pillar for decision making.
Introduction to Google Sheets as a Data Analysis Tool
Google Sheets stands out in the modern data analysis landscape, offering a dynamic and flexible platform that caters to both novice users and seasoned data analysts alike. This introduction aims to unpack the multifaceted nature of Google Sheets, spotlighting its role as a pivotal tool for data analysis and reporting within contemporary organizations.
The Appeal of Google Sheets
At its core, Google Sheets combines the ease of use with sophisticated analytical capabilities, wrapped in a cloud-based package. This unique combination ensures that data is not only accessible from anywhere but also facilitates an environment where collaboration and up-to-the-minute data analysis thrive.
Comparing Google Sheets to Alternative Tools
- Accessibility and Collaboration: Google Sheets sets itself apart from traditional desktop-based spreadsheet software through its inherent design for collaboration. Multiple users can engage with the same dataset in real time, offering a transparent and unified approach to data analysis that is hard to replicate in standalone applications.
- Integration and Add-ons: Beyond its native features, Google Sheets boasts an expansive ecosystem of add-ons and seamless integration with the broader suite of Google services. This opens up a realm of possibilities, from automating data import from various sources to enhancing data visualization and analysis capabilities, making it a highly extendable platform for specialized analytical needs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: One of Google Sheets’ most compelling attributes is its affordability. Available free of charge with a Google account and part of the broader Google Workspace for organizations, it provides a cost-effective solution without compromising on functionality or performance.
Empowering Data Analysis and Reporting
- Real-Time Collaboration: Google Sheets eradicates the barriers of traditional spreadsheet tools, promoting a culture of cooperation and shared insights. This real-time collaboration functionality not only speeds up the data analysis process but also fosters a more inclusive and dynamic decision-making environment.
- Advanced Analytical Tools: With support for everything from simple arithmetic calculations to more complex statistical analysis, Google Sheets is well-equipped to handle a broad spectrum of data analysis tasks. Pivot tables, conditional formatting, and an array of built-in functions allow users to dig deeper into their data, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
- Visualization Capabilities: Google Sheets excels in transforming raw data into compelling visual narratives. Its robust charting and graphing tools enable users to create a variety of visual data representations, from simple bar charts to intricate scatter plots, making it easier to convey complex data stories in an understandable and engaging manner.
In summary, Google Sheets is not just a spreadsheet application but a comprehensive data analysis solution. Its blend of accessibility, integrative capacity, and advanced analytical and visualization tools make it an indispensable asset for any data-driven organization looking to harness the power of their information for strategic decision-making.
Setting Up Your Data Environment in Google Sheets
Initiating your journey into data analysis with Google Sheets begins by laying a robust groundwork. This essential phase involves preparing your spreadsheet for the intricate tasks ahead, ensuring your data is accurate, organized, and primed for analysis. Here’s how to effectively set up your data environment in Google Sheets.
Importing and Organizing Data
- Data Importation: Google Sheets supports importing data from a multitude of sources, streamlining the transition of information into your spreadsheet. Whether you’re working with CSV files, Excel spreadsheets, or extracting data from web pages, Google Sheets simplifies the process. To import data, utilize the “File” menu, select “Import,” and choose from the available options to bring your data directly into the platform. This seamless integration ensures that your starting point is solid and comprehensive.
- Organization Techniques: The initial setup of your spreadsheet is pivotal. Begin by applying clear naming conventions to your sheets and ranges to avoid confusion later on. Organize your data logically, using separate tabs for different datasets or stages of analysis. Consider categorizing your data to facilitate easy navigation and analysis. Proper organization from the start enhances the clarity and efficiency of your data analysis process.
Cleaning and Preparing Your Data
- Data Cleaning: The integrity of your analysis hinges on the quality of your data. Start by scrutinizing your dataset for inaccuracies or inconsistencies. Utilize Google Sheets’ functionalities to identify and correct errors, eliminate duplicate entries, and address missing values. Tools such as “Find and Replace“, conditional formatting, and simple formulas can aid in detecting and rectifying common data issues. Ensuring your data is clean not only improves the accuracy of your analysis but also prevents misleading results.
- Data Validation: To maintain the quality of your data throughout the analysis, leverage Google Sheets’ data validation tools. These features allow you to set specific criteria for what data can be entered into a cell range, such as restricting inputs to numbers, dates, or selections from a drop-down list. Data validation acts as a safeguard, minimizing the risk of errors or inconsistent data entries as your dataset evolves. It’s a proactive step towards preserving the integrity of your analysis.
By meticulously importing, organizing, cleaning, and validating your data in Google Sheets, you lay a solid foundation for insightful and accurate data analysis. This preparatory phase is crucial for transforming raw data into meaningful insights, setting the stage for advanced analysis, visualization, and ultimately, informed decision-making.
Analyzing Data in Google Sheets
Once your data environment is meticulously prepared in Google Sheets, the next step is to harness the platform’s robust analytical capabilities. From basic calculations to intricate data manipulations and visualizations, Google Sheets offers a comprehensive suite of tools for deep data analysis. Let’s delve into how you can leverage these features to uncover insights.
Utilizing Formulas and Functions
- Basic Calculations: The foundation of any data analysis involves understanding and applying fundamental formulas. Functions like
SUM(),AVERAGE(), andCOUNT()are essential for performing basic calculations that aggregate your data, providing a quick overview of your dataset’s numerical landscape. - Advanced Functions: For more nuanced data manipulation and analysis, Google Sheets supports a variety of advanced functions.
VLOOKUP(),INDEX(MATCH), and conditional functions such asIF()andSUMIF()allow for sophisticated data queries and condition-based calculations. These functions are instrumental in filtering data, matching and looking up values across different datasets, and performing complex conditional analyses.
Leveraging Pivot Tables for Data Summarization
- Creating Pivot Tables: Pivot tables are powerful tools in Google Sheets for summarizing, analyzing, sorting, and presenting large datasets. They enable you to dynamically rearrange data, making it easier to compare and contrast different variables. Setting up pivot tables involves selecting your data range and navigating to “Data” > “Pivot table report”. This initiates a new tab where you can define rows, columns, values, and filters to organize your data summary effectively.
- Analyzing Trends: With pivot tables, you can effortlessly identify trends, patterns, and outliers within your dataset. They are particularly useful for breaking down complex data into more manageable summaries, allowing for a clearer understanding of the underlying trends and facilitating data-driven decision-making.
Visualizing Data with Charts and Graphs
- Chart Selection: Visual representation of data can significantly enhance the comprehensibility of your analysis. Google Sheets offers a myriad of chart types, including bar, line, pie, and scatter plots, among others. Selecting the appropriate chart type is crucial for effectively conveying the insights you’ve derived from your data.
- Customization Techniques: Beyond basic chart creation, Google Sheets allows for extensive customization of charts and graphs. This includes adjusting chart elements like axes, labels, and colors, as well as applying advanced options such as trendlines or error bars. Customizing your charts ensures that they not only accurately represent your data but also resonate with your audience by highlighting the most pertinent insights.
By mastering these analytical techniques in Google Sheets, you’re equipped to perform comprehensive data analysis, from straightforward calculations to advanced data manipulation and insightful visualization. Whether you’re summarizing large datasets with pivot tables or illustrating trends through customized charts, Google Sheets facilitates a versatile and powerful platform for making data-driven decisions.
Advanced Google Sheets Features for Deeper Analysis
For users ready to elevate their analytical workflows, Sheets offers advanced tools that help automate, scale, and refine insights.
1. QUERY: SQL Power Inside Sheets
QUERY lets you filter, sort, group, and aggregate data using SQL‑like syntax.
Example: Summarize total sales by product:
2. Add-ons for Extended Functionality
Popular options:
- Supermetrics → Marketing and analytics imports
- Google Analytics → Website performance data
- Power Tools → Bulk cleanups and transformations
3. Automate Workflows with Apps Script
Apps Script allows you to:
- Refresh data automatically
- Build custom functions
- Push/pull API data
- Trigger workflows based on time or user actions
By mastering these advanced features, you’re not just using Google Sheets as a spreadsheet tool; you’re leveraging it as a powerful platform for data analysis and automation. The QUERY function, along with strategic use of add-ons and custom scripts with Google Apps Script, can transform your approach to data analysis, making it more efficient, dynamic, and tailored to your unique requirements.
Crafting Insightful Reports and Dashboards
The final step in data analysis within Google Sheets involves distilling your complex data into digestible, actionable insights through well-designed reports and dynamic dashboards. This section outlines the best practices for creating these essential tools, ensuring they are both informative and engaging.
Best Practices for Designing Reports
- Clarity and Conciseness: The effectiveness of a report hinges on its readability. Use clear headings to structure your content, concise descriptions to explain your findings, and bullet points or highlighted text to draw attention to key insights. This approach ensures that readers can quickly grasp the essence of your analysis without getting lost in the details.
- Data Visualization: A picture is worth a thousand words, especially in data analysis. Select charts and graphs that best represent your data, considering the story you want to tell. For example, use line charts to depict trends over time, bar charts for comparisons among categories, and pie charts to show proportions. Properly labeled axes and a legend are must-haves to make your visualizations comprehensible.
- Customization for Audience: Tailor your reports and dashboards to the specific needs and expertise level of your audience. Decision-makers might require a high-level overview with strategic insights, whereas technical teams may need detailed data to implement changes. Customize the depth of information and the complexity of data visualizations accordingly.
Sharing and Collaboration Features
- Real-time Collaboration: Google Sheets excels in facilitating collaborative efforts. Utilize its sharing features to work on reports and dashboards with team members in real time. This collaborative approach not only enhances the quality of the final product through diverse inputs but also ensures all stakeholders are on the same page.
- Access Control and Sharing: Google Sheets allows you to manage access rights meticulously, ensuring data security and controlled collaboration. You can set permissions for who can view, comment, or edit your documents. This level of control is crucial when dealing with sensitive information or when coordinating between different departments or teams. The idea is to prevent data harvesting without consent and with wrong intentions.
Exporting and Publishing Reports
- Export Options: Google Sheets supports various formats for exporting reports, including PDF, Excel, and CSV, among others. Choose the format that best suits your needs or the preferences of your report’s recipients. For instance, PDFs are ideal for distribution, while Excel files may be preferred for further analysis.
- Publishing to the Web: For broader dissemination or public access, Google Sheets offers a “Publish to the web” feature. This option allows you to share your reports and dashboards with people outside your organization without compromising the integrity of your original data. It’s an excellent way to provide stakeholders with live, interactive access to your findings.
By following these best practices, you can leverage Google Sheets to create reports and dashboards that not only communicate your data-driven insights effectively but also foster a culture of informed decision-making within your organization.
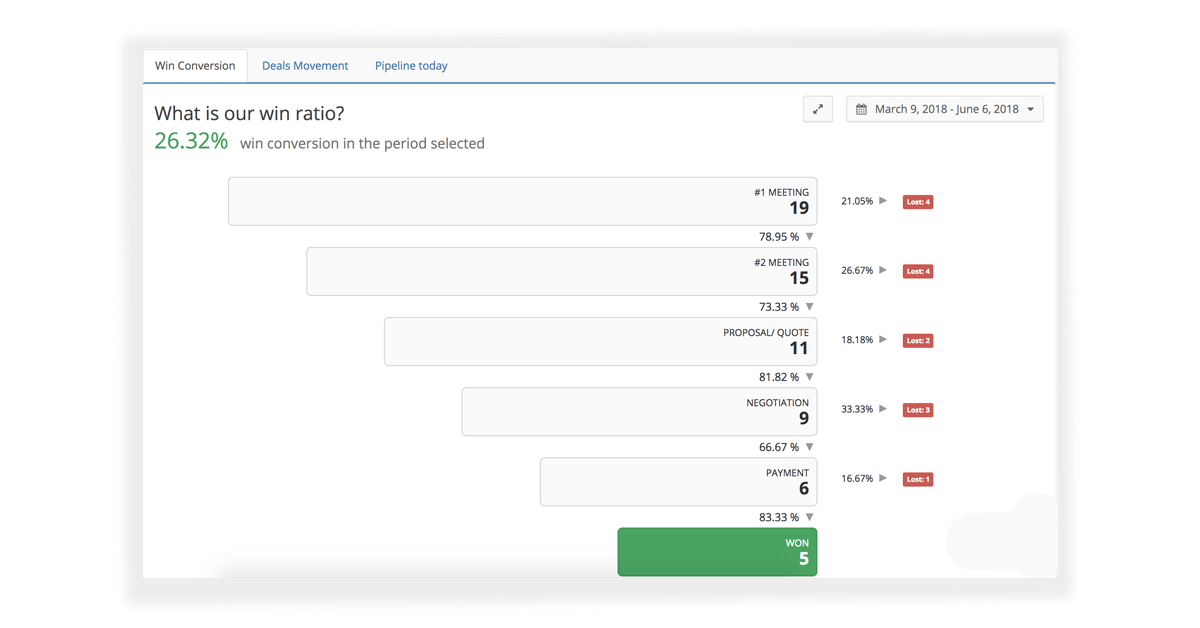
Exploring Alternatives: Teamgate CRM’s Sales Insights and Analytics
While Google Sheets serves as a versatile platform for a wide array of data analysis and reporting tasks, the specialized demands of sales-focused organizations often necessitate more tailored solutions. Teamgate CRM emerges as a compelling alternative, offering a suite of features specifically designed to enhance sales tracking, customer relationship management (CRM), and analytics.
Introduction to Teamgate CRM
- Overview of Teamgate CRM: Teamgate CRM provides an all-encompassing solution for sales teams, blending seamless sales tracking capabilities with robust customer relationship management. Its platform is engineered to streamline the sales process, offering intuitive tools for every stage of the sales journey, from lead capture to deal closure. The integrated analytics feature goes beyond mere data collection, delivering deep insights into sales performance and customer engagement.
- Sales Insights Features: At the heart of Teamgate CRM’s value proposition are its advanced sales insights features. These include comprehensive lead scoring systems that help prioritize prospects based on their likelihood to convert, detailed sales pipeline analysis that offers visibility into every stage of the sales process, and performance tracking to monitor sales activities and outcomes. These features empower sales teams to make informed decisions, focus their efforts where they are most needed, and continuously optimize their sales strategies.
Analytics and Dashboards in Teamgate CRM
- Customizable Dashboards: Teamgate CRM stands out with its highly customizable dashboards, providing real-time visibility into critical sales metrics, team performance, and customer interactions. These dashboards can be tailored to meet the specific needs of your sales team, allowing for the monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) that matter most to your organization. The ability to customize views and reports ensures that every team member has access to the insights they need to drive sales effectively.
- Advanced Analytics Tools: Beyond standard reporting, Teamgate CRM offers advanced analytics tools designed to elevate sales strategy with forecasting, trend analysis, and actionable insights. These tools enable sales teams to anticipate market changes, identify sales opportunities, and make data-driven decisions to propel growth. The analytics suite in Teamgate CRM is both powerful and user-friendly, making sophisticated data analysis accessible to all team members.
Efficiency and Integration
- Streamlining Sales Processes: Efficiency is key to sales success, and Teamgate CRM addresses this by automating repetitive tasks, managing leads more effectively, and facilitating seamless communication with prospects and customers. This automation not only saves time but also reduces the likelihood of errors, ensuring that sales teams can focus on building relationships and closing deals.
- Integration Capabilities: One of Teamgate CRM’s strengths is its ability to integrate with a wide range of tools and platforms, including email marketing software, social media platforms, and customer support tools. This ecosystem approach ensures that sales teams have a unified platform that encompasses all aspects of the sales and marketing process, enhancing collaboration and driving more cohesive sales strategies.
Teamgate CRM offers a specialized, feature-rich platform for sales-focused organizations looking for an alternative to Google Sheets for their sales insights and analytics needs. With its comprehensive suite of CRM features, advanced analytics, and emphasis on efficiency and integration, Teamgate CRM is well-positioned to help sales teams achieve their objectives and drive business growth when transitioning from Google Sheets.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of data-driven decision making with Google Sheets and the potential of specialized tools like Teamgate CRM, it’s clear that the landscape of business intelligence and analytics is both vast and varied. The choice between Google Sheets and other platforms depends on specific organizational needs, the complexity of data, and the depth of insights required.
Whether you’re just beginning your journey with data analysis or looking to enhance your organization’s sales strategies with advanced analytics, the tools and techniques discussed here offer a solid foundation. Embrace the power of data to unlock new opportunities, drive efficiency, and foster a culture of informed decision making within your organization.
FAQs: Google Sheets for Analytics
1. What are the key benefits of data-driven decision making over intuition-based methods?
Answer: Data-driven decision making offers several advantages over intuition-based methods by providing a more objective foundation for decisions. These benefits include enhanced market responsiveness, enabling organizations to quickly identify and capitalize on emerging trends; improved customer experiences through personalized services; increased operational efficiency by identifying and addressing inefficiencies; and fostering innovation by uncovering insights that can lead to new product developments and market opportunities. This approach minimizes biases and errors that can arise from relying solely on intuition.
2. How can I import and clean my data in Google Sheets?
Answer: To import data into Google Sheets, you can use the “File” menu and select “Import,” where you have options to upload files, connect to Google Drive, or even import data from the web. Cleaning data involves several steps, including removing duplicates using the “Remove duplicates” tool under the “Data” menu, fixing errors manually or with functions like TRIM() for removing extra spaces, and handling missing values by either deleting rows, filling them with a placeholder, or using formulas to estimate values. Data validation features can also help maintain data quality by restricting the types of data entered into specific cells.
3. What are the most useful Google Sheets formulas for data analysis?
Answer: Some of the most powerful formulas for data analysis in Google Sheets include:
VLOOKUP()for finding data in a table or range by row.INDEX(MATCH())for more flexible lookups thanVLOOKUP.QUERY()for running SQL-like queries on your data.- Aggregate functions like
SUM(),AVERAGE(),COUNT(),MAX(), andMIN()for basic statistical analysis. - Conditional functions like
IF(),COUNTIF(),SUMIF(), andAVERAGEIF()for performing calculations based on specific criteria.
4. Can Google Sheets handle large datasets for analysis?
Answer: Google Sheets can handle datasets up to 10 million cells. For most users and use cases, this is sufficient. However, performance may slow down as you approach this limit, especially if using complex formulas or functions. For very large datasets or more complex data analysis tasks, you might need to consider using more robust data analysis tools or databases.
5. How do I create and interpret pivot tables in Google Sheets?
Answer: Creating a pivot table in Google Sheets involves selecting your data range and then navigating to “Data” > “Pivot table.” From there, you can add rows, columns, values, and filters to organize your data summary. Interpreting pivot tables is about understanding the summarized data – for example, sales data could be summarized by product and month to easily see which products perform best over time. Pivot tables are powerful for spotting trends and making comparative analyses without altering the original data.
6. What are some advanced features of Google Sheets for data analysis?
Answer: Advanced features of Google Sheets include the QUERY function for complex data manipulation, Google Apps Script for automating tasks and custom functions, and the extensive library of Add-ons that can extend its functionality for specific analysis needs, such as data visualization, project management, and integration with external data sources like Google Analytics.
7. How does Teamgate CRM complement data-driven decision making in sales?
Answer: Teamgate CRM complements data-driven decision making in sales by offering specialized tools for managing customer relationships, tracking sales processes, and analyzing performance through sales insights and analytics. It provides customizable dashboards for real-time sales metrics, lead scoring for prioritizing prospects, and detailed analytics tools for forecasting and trend analysis, making it easier to make informed decisions and strategize effectively based on data.
8. Are there any limitations of using Google Sheets for sales data analysis compared to Teamgate CRM?
Answer: While Google Sheets is versatile and powerful, it has limitations compared to a specialized tool like Teamgate CRM, especially in handling large volumes of sales-specific data, automating sales processes, and providing real-time insights and analytics tailored to sales teams. Google Sheets requires manual setup for sales tracking and analysis, whereas Teamgate CRM offers out-of-the-box solutions designed specifically for sales efficiency and analytics.
9. How can Teamgate CRM’s analytics and dashboards improve sales performance?
Answer: Teamgate CRM’s analytics and dashboards provide a 360-degree view of sales activities, customer interactions, and performance metrics. By offering real-time insights into sales pipeline, lead quality, team performance, and customer behavior, it enables sales teams to make data-driven decisions that improve efficiency, prioritize efforts on high-value prospects, and ultimately drive higher sales performance. Customizable dashboards allow for monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with sales goals and objectives.
10. What factors should be considered when choosing between Google Sheets and Teamgate CRM for data analysis and reporting?
Answer: When choosing between Google Sheets and Teamgate CRM, consider factors such as the specific needs of your sales team, the volume of data you’re managing, the complexity of the analysis required, and your budget. Google Sheets is a great low-cost, flexible tool for various data analysis tasks and is ideal for businesses just starting with data analysis or those with limited needs. In contrast, Teamgate CRM offers specialized sales insights, analytics, and dashboard capabilities that are better suited for organizations looking to streamline their sales processes, automate tasks, and gain deeper insights into their sales data.
 Basic Formula Examples
Basic Formula Examples
 Elegantly Handling Errors with IFERROR
Elegantly Handling Errors with IFERROR